Starting with software version 3.1.3.2.0 on the EcoSGE platform (NAT, BRAS, QoE, URL Filter), the onstick mode of operation is supported, which can significantly save carriers on the purchase of additional ports for routers. In previous versions, only the inline mode was supported, which in many cases led to the inefficient use of expensive ports in routers to which EcoSGE devices were connected.
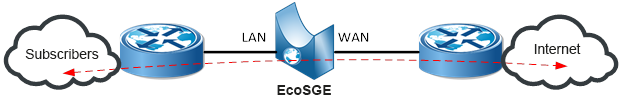
In inline mode, the EcoSGE device connects to the gap of one or more existing links between two different routers:
or between the same router:
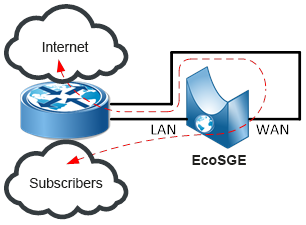
Anyway, on routers to connect an EcoSGE device, two ports are used for a single link, into which EcoSGE “crashes”. The port of the EcoSGE device that “looks” towards the subscribers is called LAN, and the port looking towards the Internet is called WAN.
Due to the fact that in almost all networks of communication operators, Downstream traffic (from the Internet to subscribers, WAN -> LAN) is superior to Upstream traffic (from subscribers to the Internet, LAN-> WAN), the inline scheme leads to asymmetric utilization of ports – both ports of the router are heavily loaded in one direction and significantly less loaded in the opposite direction:
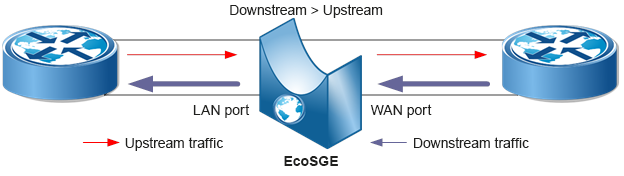
Considering this drawback of the inline-mode of operation, the onstick mode was implemented:
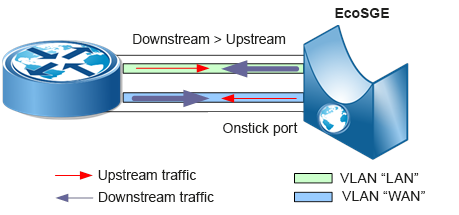
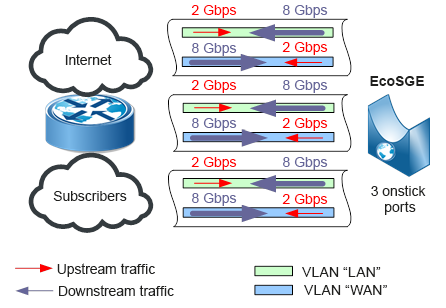
In onstick mode, in one port of the EcoSGE device, both WAN -> LAN traffic (in VLAN “WAN”) and LAN -> WAN traffic (in VLAN “LAN”) are transmitted.
If we accept that Upstream traffic accounts for 25% of Downstream traffic, then calculations show that with almost any value of the Downstream traffic value, it is more advantageous to use the onstick mode. For example, if Downstream traffic in NNI is 24 Gb / s, then to pass it through an EcoSGE device inline, you need to use 6 ports on the routers (3 ports for connecting EcoSGE LAN ports and 3 more ports for connecting WAN ports):
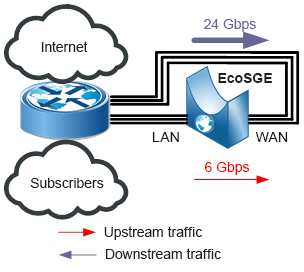
At the same time, traffic going through the ports of routers in the Upstream direction will be equal to only 6 Gbps, while the resources spent for this could pass up to 30 Gbps of traffic.
In onstick mode, to pass the same amount of traffic through the EcoSGE device, you need only 3 ports on the router:
Date of a post: 07.02.2019
Tags: EcoSGE onstick Service Gateway Engine Solution
Contacts for press: pr@rdp.ru
Share the news on social networks and messengers